Columns tab
The Columns tab is where you define the column content and header content for each column in a table, such as a parts list, hole table, bend table, block table, or user-defined table. You also can specify the display format of each column, the value formatting of property text, and the order that the columns appear in the table. To learn how you can use these options, see the help topic, Using the Columns tab.
- Columns
-
Lists the columns currently defined in the table. This also shows the order in which the columns will appear.
Note:All the other controls are based on the currently highlighted column in this list.
- Move Up
-
Moves the selected column up one position in the Columns list.
In the table, this has the effect of moving the column to the left.
- Move Down
-
Moves the selected column down one position in the Columns list.
In the table, this has the effect of moving the column to the right.
- Add Column
-
Adds the property type selected in the Properties list to the Columns list.
- Delete Column
-
Removes the selected column from the Columns list and from the table.
- Properties
-
Lists all the available file properties, material properties, feature-specific properties, and design properties associated with the different types of assembly models. For example:
-
Model document properties, such as file name, file size, company, document number, and author.
-
Properties defined in the files referenced by the parts list, for example, material type and custom material properties.
-
Standard parts list properties: item number, quantity, cut length, total length, item mass, quantity mass, and miter angles.
-
Standard bend table properties: sequence number, acute angle between faces, outside angle, bend direction, radius, and feature.
-
Information about rigid and flexible (adjustable) tubes and hoses, including the flattened length of each (cut length), tube bend radius, tube inside cross-section area, tube outer diameter, and tube wall thickness. For more information, see Create a parts list for flexible hoses and tubing.
-
Information derived from members of a family of assemblies, including the FOA member names and numbers, and component names and their states. For more information, see Create a family of assemblies parts list.
-
Properties of holes added to a part model, such as hole type, size, location, and distance from a specified model location. You also can specify what type of information you want to show in the hole callouts attached to the holes on the drawing.
-
Exposed variable values defined in the Variable Table. These property names are appended with the text, (Exposed Variable). For more information, see Expose a variable.
-
Custom material properties defined in the Material Table, and custom properties defined on the Custom tab in the File Properties dialog box. These property names are appended with the text, (Custom Property) and (Custom Material Property), respectively. To learn how you can use these properties, see Example: Show custom properties and materials in a parts list and Example: Show sheet metal material thickness in a parts list.
-
Custom occurrence properties defined in the Occurrence Properties dialog box in an assembly. These property names are appended with the text, (Occurrence Property).
Note:Select the User Defined property to create a column with no predefined properties. With a user-defined column, you can enter and edit the content in every data cell. For more information, see Create a column for user-defined content.
-
- Column Format
-
The following options control how the column highlighted in the Columns list appears in the table or parts list.
- Show column
-
Shows or hides the selected column.
- Column width
-
Sets the width of the selected column.
- Headers
-
The options in the Headers section define the general characteristics of all column headers in the table.
- Show header
-
Shows or hides the column header on the column.
- Position
-
Specifies where to display the column header:
-
Header: At the top of the column.
-
Footer: At the bottom of the column.
-
Both: At the top and bottom of the column.
-
Neither: Not displayed.
-
- Fixed header row height
-
Specifies that the header row maintains the height entered in the box at right. This is independent of text height.
This option affects all headers in the table.
-
When columns are displayed with a two-row header, the height of each of the rows is the value specified by the Fixed header row height box.
-
When column headers are displayed with a combination of single and double rows, the single-row column headers are the same height as the combined, two-row column headers.
-
- Number of rows
-
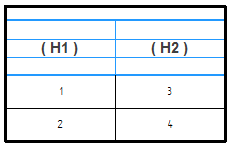
Specifies the total number of header rows for all table columns. The default number of header rows is one. You can have up to five header rows.
Example:In the following example, there are four header rows, which are shown in blue. Row four is the row that is adjacent to the column data.
- Column Header
-
The options in the Column Header section define the content and merging of the header for the currently selected column.
- Text row
-
Identifies the working header row number for the purpose of defining content in the Text box, changing cell alignment using the Format Table Cells dialog box, and merging headers across multiple columns.
- Text
-
Specifies the header text for the column. The default header is the same as the selected property. You can type in this box to change it.
You can create multiline headers using the Enter key.
- Merge with next horizontal cell
-
Merges column headers horizontally across multiple columns. Use this option to merge two or more adjacent headers into one.
Columns are merged from left to right, in the order in which they are displayed in the table. The formatting of the first column with the Merge with next header box checked controls the appearance of the merged columns.
For examples, see Manipulate table rows and columns.
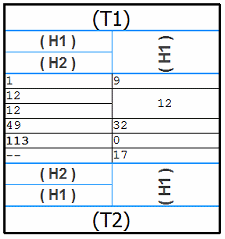
- Merge with next vertical cell
-
Merges column headers vertically across multiple rows.
Use this option to merge a header cell on the current row with the adjacent header cell on the next row.
Example:You can use the two Merge with options to arrange column header cells (H1) and (H2) differently for each column.
- Format Cells
-
Opens the Format Table Cells dialog box for you to specify the text alignment and orientation of the currently selected header cell in the currently selected column.
- Column Data
-
The options in the Column Data section define the content and output value formatting of the currently selected column.
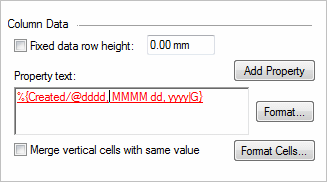
- Fixed data row height
-
Specifies that the data cells in the column maintain the height specified in the box at right, and that they do not change height when the text height changes.
This affects all data cells in the table, not just the current row or current column.
- Property text
-
Specifies the property text definition in the currently selected column.
-
When you select a column, the property text code that is used to fetch the data is displayed in the Property text box.
-
You can type plain text and punctuation in the Property text box. You can copy and paste into the box.
-
You can concatenate property text strings in a single column by selecting and adding individual Properties, one by one, using the Add Property button. For more information, see Combine properties in a column.
-
- Add Property
-
Adds the property text string displayed in the Property text box to the content definition for the column that is currently selected in the Columns list.
- Format
-
Opens the Format Values dialog box for you to choose the formatting to apply to the resolved property value when it is displayed in the table. This button is available when you click within the property text string in the Property text box.
You can apply formatting to each valid property text string. The type of formatting you can apply depends on your cursor position when you select the Format button. For example, you can display text such as the file name or document title in all UPPERCASE letters. You also can apply month-day-time formatting to a date value.
For more information, see the help topic, Format property text values.
- Merge vertical cells with same value
-
When two adjacent table cells in the same column have the same value, merges the two cells vertically and displays a single value.
Example:Column 1 shows unmerged data cells. Column 2 shows merged data cells.
Column 1
Column 2
9
9
12
12
12
Note:This option does not merge cells when the following check box also is selected on the General tab: Wrap table data cells to new row.
- Format Cells
-
Opens the Format Table Cells dialog box for you to specify the alignment of all data cells in the currently selected column.
© 2021 UDS