Tutorial: Compare displacement load results for different materials
-
Open the file FE_Displacement.par.
Simulation models are delivered in the \Program Files\UDS\QY CAD 2022\Training\Simulation folder.
-
Create a linear static study.
-
From the Material list on the Simulation tab→Study group, select Aluminum, 1060.
-
Select the New Study command.
-
Choose the Linear Static study type and Tetrahedral mesh type. Select OK.
-
-
Add a displacement load.
-
Select Simulation tab→Structural Loads group→Displacement
 .
.The Loads command bar is displayed.
-
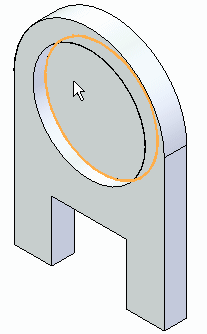
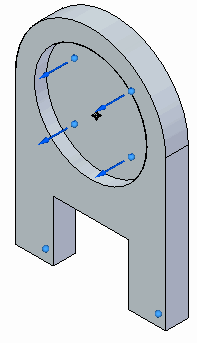
Select the circular face shown.
-
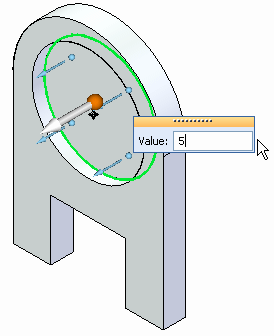
Type 5 mm for the displacement value.
-
Ensure the directional vector points away from the part.
-
On the command bar, ensure the pinned constraint button is selected
 .
.This creates a pinned constraint for the face.
Note:NX Nastran requires that a displacement load has a matching constraint on the part. In QY CAD Simulation, the Displacement command automatically generates the required constraint if you also select the Pinned option on the command bar.
-
Press Enter to accept, and then click in space to finish.
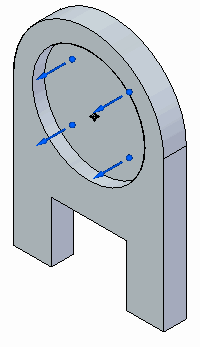
The Displacement 1 load is displayed in the Simulation pane.

-
-
Define a fixed constraint on two faces.
-
Select Simulation tab→Constraints group→Fixed.
-
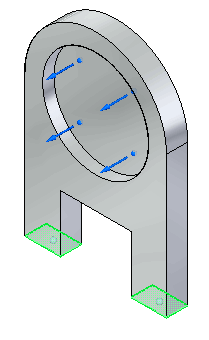
Select the two end faces as shown.
-
Right-click to accept, and then click to finish.
-
-
Mesh and solve the study.
-
In the Simulation pane, turn off constraints and loads.
-
Select the Mesh command. Choose Mesh & Solve.
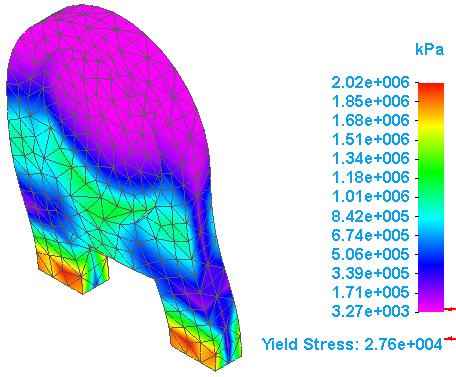
After a few moments, the part is meshed and solved. The results are displayed in the Simulation Results environment.
-
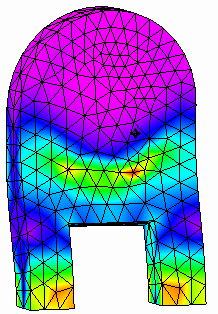
Rotate the part to view the areas of highest stress.
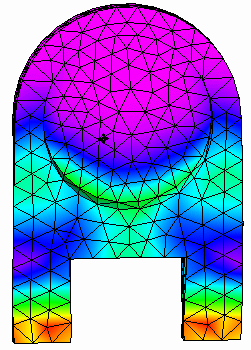
-
Select Home tab→Output Results group→Create Report.
-
In the Create Report dialog box:
-
Change the default title in the Report title box to Simulation Report - Static Study 1
-
In the Author box, type your name or initials.
-
In the Introduction box, type Simulation results using Aluminum 1060.
-
Browse to and select the folder location where you want to save the report.
-
Click Create Report.
-
-
On the ribbon, click Close Simulation Results.
-
-
Create a second study with a different material and repeat the analysis.
Note:For this activity, you will simply create a second study in the same document and change the material. Changing the material in a second study causes the first study to go out of date. Alternatively, if you want to compare and contrast the physical behavior of different materials under identical load and constraint conditions, you can copy the part to a separate file and then change the material there.
-
In the Simulation pane, right-click Static Study 1 and choose Create Copy.
The duplicated study is added at the bottom of the Simulation study navigator pane and named Static Study 2. The displacement load and fixed constraint are copied with it.

-
Change the material for Static Study 2 to Nylon, general purpose.
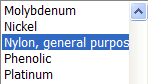
If the material is not shown in the Material List, then select it from the Material Table by doing the following:
-
On the Simulation tab→Study group, click Material Table
 .
. -
In the Material Table, on the Material Properties tab, expand the Non-metals folder, and then expand the Plastics folder.
-
In the Plastics folder, click
 Nylon, General purpose, and then click the Apply to Model button.
Nylon, General purpose, and then click the Apply to Model button.
-
-
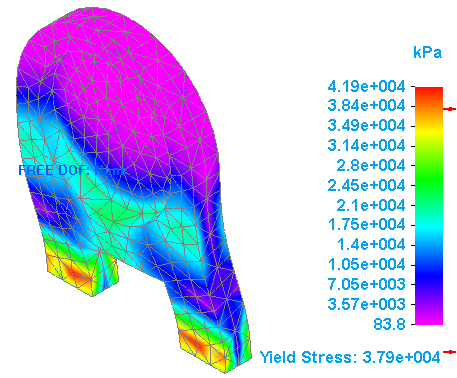
Solve the part as you did for Static Study 1.
-
To save the second set of results, create another report, and type Simulation results using Nylon, general purpose in the Introduction box. You also can type information in the Conclusion box, based on the results.
-
-
Open both report files to compare the difference in stress value between the part made from aluminum versus the part made from nylon.
Note:The use of nylon for the material would be more appropriate for this application.
-
Close this file.
In this activity, you will use the Create Copy command to create two studies within a single document to compare the stress results of two different materials when a displacement load is applied. You will use the Create Report command to preserve the results in two separate report files.
© 2021 UDS