Opening non-QY CAD documents
QY CAD opens data from other CAD systems. You can open both 2D and 3D data in the different QY CAD environments.
You can open the following types of files in QY CAD:
| File Format | Environment | Comments | Related User Interface |
|---|---|---|---|
| .dxf .dwg | Draft | .dxf and .dwg format files can be opened in the Draft environment as 2D geometry. The translation options available for these files vary based on the creation methods of the originating CAD system. You can generate .dxf and .dwg files in systems other than AutoCAD. The Draft environment will open .dxf and .dwgfiles created in AutoCAD version 12 through AutoCAD 2011. Solids created with Autodesk are output to .sat format as they are encountered in the AutoCAD file. | |
| .stp, .step | Part Sheet Metal Assembly | STEP (.stp, .step) standards AP203 class II - class VI entities, AP214 class II - class VI entities, and STEP assemblies are supported by QY CAD. | |
| .igs, .iges (2D or 3D) | Draft (2D) Part (3D) | IGES (.igs, .iges) 2D and 3D files are supported by QY CAD. IGES 2D files are opened in the Draft environment and IGES 3D files can be opened in the Part, Assembly, or Sheet Metal environments. IGES is an industry-standard neutral format. This data can be imported as construction wireframe, construction surfaces, or solids depending on the modeling techniques and formats supported by the originating CAD system. | |
| .x_b .x_t | Part Sheet Metal Assembly | The supported versions of Parasolid increase as subsequent versions of QY CAD are built on the latest version of Parasolid. Parasolid files can be opened as a solid body feature in the Part, Assembly, and Sheet Metal environments. | |
| .prt (NX) | Part Sheet Metal Assembly | NX (.prt) files are also based on the Parasolid kernel and can be opened as solid feature bodies in the Part, Assembly, or Sheet Metal environments. | |
| .sat (ACIS) | Part Sheet Metal Assembly | ACIS (.sat) files created in versions 3–19 are supported by QY CAD. | |
| .prt (Pro/E) | Part Sheet Metal Assembly | Pro/ENGINEER (.prt) files created in versions 17-Wildfire version 5 are supported by QY CAD. | |
| .plmxml (XML) | Part Sheet Metal Assembly | ||
| .model (Catia V4) | Part Sheet Meal Assembly | ||
| .catpart, *.catproduct (Catia V5) | Part Sheet Meal Assembly | ||
| .sldprt .sldasm | Part Assembly | SolidWorks | Import Options for SolidWorks (.sldprt and .sldasm) dialog box |
| .jt | Part Sheet Meal Assembly | JT (Visualization Format) | |
| .stl | Standard Template Library | ||
| .ipt, .iam | Part Draft Sheet Meal Assembly | Inventor |
Opening foreign documents that contain multiple bodies
When you open a foreign document, QY CAD checks to determine if the file being opened contains multiple bodies. If the file contains multiple bodies and you are using a QY CAD part (.par) template to open the file, a warning dialog box displays. You can continue the translation using the part template or return to the Open File dialog box and open the foreign file with a QY CAD assembly (.asm) template.
Controlling how foreign bodies are imported
QY CAD provides options to the translator import option dialog boxes that allow you to control how foreign bodies are translated during import. You can stitch, group curves, or boolean multiple bodies together. You can also specify if you want to use the imported body as a base feature for your QY CAD model. You should be careful when you select these options to ensure you get the desired results.
If you select the Stitch on Import option, QY CAD unites the multiple surfaces or sheets together. It may be to your advantage not to stitch on import, but to evaluate what you need to stitch, and perform the stitch after you import the file to Solid Edge.
If you select the Group Curves in a Single Part Copy option, QY CAD consolidates the curve data into a single part copy. This is very similar to what the Stitch on Import option does to surfaces. You might want to identify the curves that you do not need and hide or delete them before you import the file. This helps to control the amount on unused geometry in your imported file.
If you select the Boolean on Import option, QY CAD unites the multiple bodies into a single part copy.
If you select the Create Base Feature option, QY CAD uses the imported solid body as the base feature for the QY CAD model. If there is more than one solid body in the file, no base feature is created. In this case you can use the Make Base Feature command to select a solid to use as the base feature or construct a new base feature for the model.
If you clear this option, all solid bodies contained in the file you are importing are placed in PathFinder as a part copy rather than a body feature. Inserting bodies as a part copy requires you to select or create a base feature.
Since a base feature is not always created automatically, you need to be able to distinguish between the different geometry types. Symbols in the left column of PathFinder tell you the different geometry types included as a part copy. The following table explains the symbols used in PathFinder:
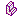 | Solid geometry |
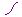 | Curve data |
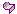 | Surface or sheet data |
Maintaining associative links when opening NX, JT, or X_T files in QY CAD
QY CAD supports associativity when importing NX, JT and X_T files. There are three ways to import these files in to QY CAD.
-
File Open using a part template file
-
Insert part copy
-
File Open using an assembly template file
File Open using a part template file
-
Using the File Open command to import documents using a part template results in a simple translation of the imported data. Solid bodies are created in QY CAD and there are no associative links back to the imported NX, JT, or X_T file.
Insert part copy
-
The Part Copy command supports both associative and non-associative translation depending on the link option on the Inter Part Copy dialog box. The Part Copy command creates solid bodies that have an associative link back to the file you are importing. Any edits made to the input file, such as adding a hole, are updated in the QY CAD file. Any new bodies added to the input file do not display in Solid Edge when the file is updated.
File Open using a part template file
-
Using the File Open command to import files using an assembly template supports both associative and non-associative translation. You can use the CreateAssociativeParts InAssembly parameter in the PSXMT.ini file to specify whether or not to link the part files back to the file being imported. An assembly is created with links to the part files in the file being imported provided that the file being imported is an assembly file.
Opening non-QY CAD documents in the Teamcenter-managed environment
When you open and save a STEP, IGES, or X_T document in the Teamcenter-managed environment, the file name is modified to correspond with the Item ID as a part of the translation process. The resulting QY CAD file is added to the same Item ID as the original foreign file. The Dataset Name is set to the default based on the business rules in place for the Dataset Name, and is updated when other key fields such as the Item Name or Document Name change. Indirect documents that are part of an assembly are assigned new Item IDs in the Upload Document dialog box. The Dataset Description automatically updates with the original file name, and the folder and project information is automatically populated for you. A Link Fixup is performed on the newly created files automatically, and your cache only contains the new files.
Dragging an unmanaged document into a managed document results in the same behavior. For example, when you select an unmanaged part from the Parts Library tab or the and drag it into a managed assembly, then save it, the Upload Document dialog displays with the values populated for you.
The data preparation tools and Add to Teamcenter remain the core of the process that validates unmanaged content and then imports it into the managed environment.
Retranslation occurs when the input file (STEP, IGES, or X_T) is updated and the translated file is reopened in QY CAD. Any new files require you to assign the necessary attribute information and then save the new documents to the database. Retranslation is always an overwrite condition. All documents are marked for upload.
IGES does not support retranslation. If the IGES file is updated, the next time the file is opened in QY CAD it is translated and created.
© 2021 UDS